CMU Dimensions Guide: Standard Concrete Block Sizes Explained
A CMU Dimensions Guide shows how important it is to know the sizes of Concrete Masonry Units (CMUs) when planning a building project. In the world, concrete blocks are one of the most popular modular building materials. This is because they are strong and can be used in many ways. The CMU block dimensions need to be correct so that they can be designed well, work with other materials, and cause less waste on the job site.The global CMU business will be worth $18.7 billion by 2033, up from $12.5 billion in 2024. Engineers, architects, and contractors must analyze dimensions to ensure CMUs are the right size for price, stability, and building design.
What Is a Concrete Masonry Unit (CMU)?
A Concrete Masonry Unit (CMU) is a standardized, precast, rectangular masonry element that includes Portland cement and aggregate. The term CMU, also known as concrete block, cinder block, or breeze block in different countries, indicates its modular features and performance standards important to modern masonry design and engineering. CMUs can be solid or have hollow cores; hollow units reduce weight and allow reinforcement and grout placement, while solid units offer higher mass and load-bearing capacity constructpedia.net. The masonry block is a general term that is used to describe any block utilized in masonry, CMU is used to refer to products produced to industry standards, which in the U.S. are typically regulated by standards such as ASTM C90 at Basalite. Proper interpretation of terminology eliminates misunderstanding in specifications, cost estimating and communication between design and construction professionals.
Where CMUs Are Commonly Used
Concrete Masonry Units are used extensively across residential, commercial, industrial, and infrastructure construction due to their structural reliability, fire resistance, and cost efficiency JMS Masonry. In residential buildings, CMUs serve as foundation walls, exterior walls, and even retaining structures where durability and thermal mass are required Dixon Incorporated-. Warehouses, retail spaces, schools and healthcare facilities in commercial and industrial industries use CMUs both as load-bearing walls and interior partitions capitalizing on sound insulation and fire-resistance characteristics. CMUs are utilized in infrastructure, landscaping, and sound-barrier walls along highways due to their tolerance to environmental loads. Their market expansion globally is evident as urban infrastructures and low-income residential buildings increasingly incorporate CMUs for improved thermal performance and cost-effectiveness. Global Growth Insights.
Nominal vs Actual CMU Dimensions
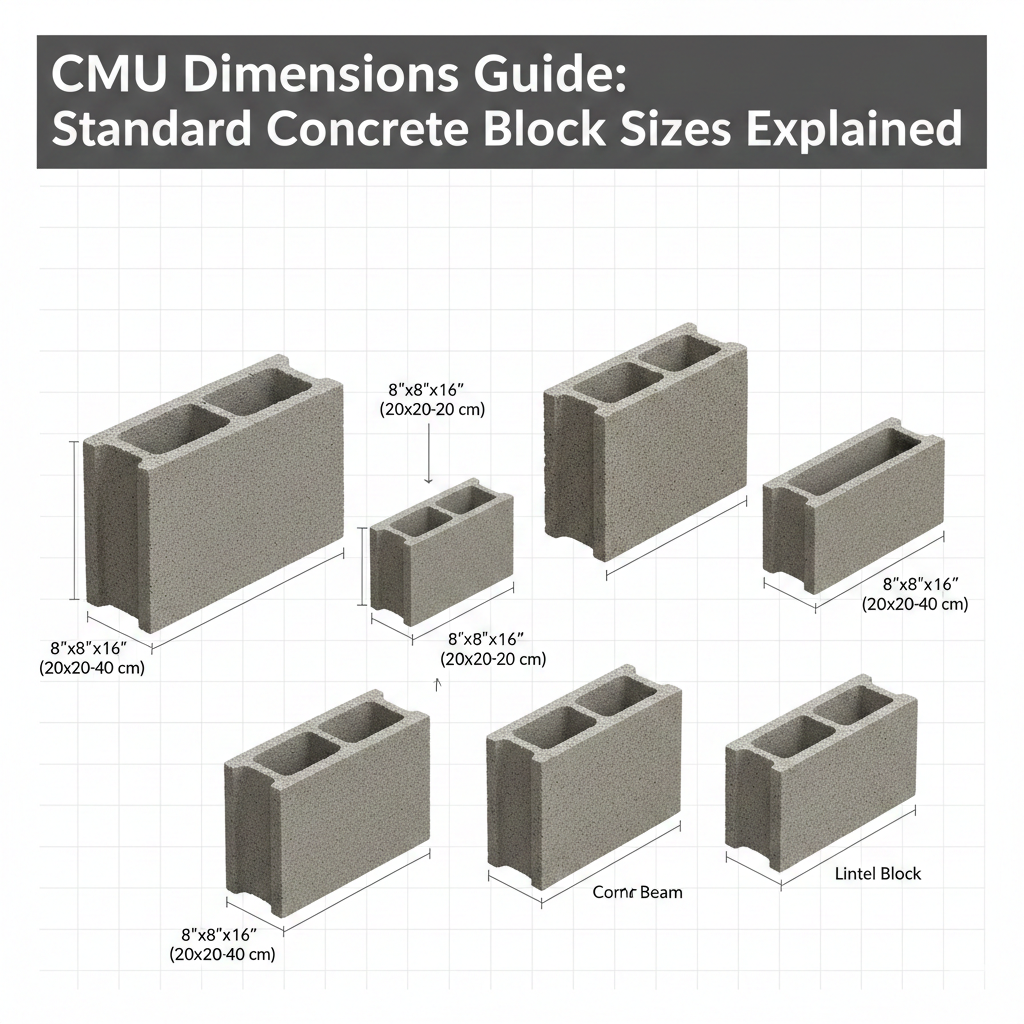
One of the most important concepts in masonry construction is the difference between nominal (Concrete block dimensions) and actual CMU dimensions.The size of the blocks with the standard mortar joint is the nominal size, and it is easier to plan and coordinate with a block in the field and on plans. To illustrate, a typical CMU could be mentioned as 8 x 8 x 16 nominal with a 3/8 mortar joint in each direction in order to support a 3/8 construction grid Archtoolbox. Most building units are approximately 3/8 inch smaller than their nominal dimensions. An 8-inch nominal block measures 7 5/8 inches in length, 7 5/8 inches in width, and 15 5/8 inches in height. This tolerance prevents material alignment issues during construction. For instance, specifying wall dimensions without considering mortar space can lead to cumulative errors and poor fit. Recognizing this difference enhances layout precision, minimizes rework, and fosters trust among construction teams.
Standard CMU Dimensions Chart
The interpretation of CMU dimensions chart assists builders, architects, and engineers to plan walls in the correct way. CMUs are constructed in nominal standard widths of 4”, 6”, 8”, 10”, and 12 inches depending on the usual building wall thickness specifications. All nominal sizes have a standard 8 inch height and 16 inch length of full blocks. The actual sizes are typically 3⁄8″ smaller than nominal in each direction to allow for the mortar joint between blocks, which keeps courses aligned on a modular grid. archdictionary.com+1
Standard CMU Dimensions Chart
| Nominal size | Actual size (inches) | Common Uses |
| 4″ x 8″ x 16″ | 3⅝″ x 7⅝″ x 15⅝″ | Interior partitions, decorative or veneer walls |
| 6″ x 8″ x 16″ | 5⅝″ x 7⅝″ x 15⅝″ | Medium loads, fire-rated partitions |
| 8″ x 8″ x 16″ | 7⅝″ x 7⅝″ x 15⅝″ | Most common for foundations & load-bearing walls |
| 10″ x 8″ x 16″ | 9⅝″ x 7⅝″ x 15⅝″ | Commercial walls & enhanced performance |
| 12″ x 8″ x 16″ | 11⅝″ x 7⅝″ x 15⅝″ | Heavy foundations, retaining walls |
Key Points
- Nominal dimensions are used in planning and specify the intended wall thickness, height, and course spacing.
- Actual dimensions are what you measure on site after accounting for the 3⁄8″ mortar joint between blocks.
- Designers often use the nominal sizes on architectural drawings to maintain consistent modular layouts and reduce cutting on site.
- The 8x8x16 CMU dimensions (nominal) represent the most widely manufactured and used block in modern construction.
Half Blocks & Special CMU Sizes
Half blocks are CMUs cut to half the nominal length of a full block typically 8″ long instead of 16″. Archtoolbox They exist so builders can:
- Reduce cutting on site at corners and wall ends.
- Maintain running bond patterns without awkward gaps.
Why They Matter
Half blocks help builders follow a modular system that aligns with other materials and openings. Archtoolbox, Without them, masons would need to see full blocks at the end of every wall slowing progress and increasing waste.
Example Use Cases
- Corners where full blocks would overshoot the layout grid.
- Wall ends and intersections to keep bond patterns neat.
CMU Shapes & Profiles
Concrete Masonry Units come in a variety of shapes and profiles to meet different construction needs. These shapes are often variations of standard blocks and help with structural or aesthetic requirements.
Common CMU Shapes
- Stretcher Blocks
These are the basic rectangular CMUs laid lengthwise in walls. - Corner Blocks
Designed for outer corners with one face exposed and the other continuing the wall. - Bond Beam Blocks
Hollow blocks with channels to pour grout and place horizontal reinforcement, adding horizontal strength to walls. - Lintel Blocks
U-shaped blocks placed over door and window openings to form a lintel beam when filled with grout and steel. - Bullnose Units
Blocks with rounded edges used to soften corners or exposed edges in design.
CMU Finishes (Appearance & Function)
Finishes on CMUs influence both looks and performance. Many of these surface options are integrated during manufacturing and comply with standard strength requirements (e.g., ASTM C90). Archtoolbox
Common CMU Finishes
- Split-Face
Rough, stone-like texture created by splitting pairs of units. Works well for exposed walls and aesthetics - Burnished (Ground Face)
Smooth surface with exposed aggregate, often used where aesthetics matter, such as facades. - Glazed Finish
Smooth, impervious surface with color options and easier cleaning, ideal for interiors or design features. - Scored or Ribbed
Grooves or ribs cut into the unit face that add visual interest and texture without full splitting.
Where They’re Used
- Split-face and ribbed units are common on commercial exteriors and landscape walls.
- Burnished and ground face finishes are used in architectural applications where appearance matters.
- Glazed CMUs are often selected for high-use interiors (e.g., schools, gyms) where wear resistance and cleanability are priorities.
Performance Benefits of CMUs (Thermal & Acoustic)
Not only is a Concrete Masonry Unit (CMU) a structure block, it also plays other important roles in building construction. When it comes to temperature comfort and soundproofing, CMUs make a big difference in wall systems. Because they contain a lot of thermal mass, they can accept and store heat during the day and release it at night, preventing temperature fluctuations. As a result, less energy is required to heat and cool buildings. It is closely related to the fact that concrete can hold more heat than lighter materials. Because of their density and design, uninsulated hollow CMU walls often have moderate R-values, which indicate thermal resistance ranging from 1.3 to 2.2 hrft³°F/Btu. This is especially true for 8-foot CMUs. This basic thermal efficiency is important across diverse climates. Also, Concrete Masonry Units (CMUs) have better Sound Transmission Class (STC) ratings when they are fully grouted and insulated. Some units can hit 60 dB. In noisy or busy places, this makes them better at blocking sound and making people feel better. Echelon Masonry+1
Industry Standards & Compliance
Industry standards assist in addressing the same by ensuring that Concrete Masonry Units are of the same quality and performance. In the United States and most other markets, the important standard is ASTM C90 that specifies minimum requirements of strength, density and dimensional tolerances of hollow and solid concrete masonry units. ASTM C90 compliance assists the designers and constructors to trust the structural capacity and durability of the walls to be predictable. Before units are sold to be constructed, manufacturers normally test them to ensure that they are up to these standards. Adherence to standards like ASTM C90 makes structural engineers, inspectors, and builders more confident that CMUs will be safe when loaded to expected loads and under expected environmental conditions. Standards also support conformity with building codes and help avoid costly mistakes or failures due to poor material quality. angelusblock.com+1
Practical Tips from Industry Experience
When working with CMU dimensions, real-world experience offers helpful planning insights that generic guides often miss. One common mistake is overlooking the 3⁄8″ mortar joint forgetting this can lead to walls that end up too long or too short compared with design drawings, requiring costly rework. Always coordinate CMU layout with windows, doors, and openings early in planning to ensure that blocks, mortar joints, and other materials align on a modular grid before construction begins.Half blocks at corners and ends also are clever so that the wall courses can end up in a nice way without having to cut half-way on site. In coordination with other trades (Mechanical or electrical), the penetration of walls into the building should be communicated early enough to create openings that can be located in areas where CMUs can support them without compromising the building. A good modular planning is not only time-saving, but it will also minimize waste of materials and enhance the quality of the construction in general.
Conclusion
Understanding CMU dimensions is essential for accurate wall layout, material planning, and long-term building performance. This guide explained how nominal and actual sizes work, why mortar joints matter, and how CMU types, shapes, and finishes affect strength, sound control, and thermal behavior. These are the same practical factors used every day by construction professionals when preparing plans and estimates. These principles of dimensions are used at US Bid Estimating and Engineering which is located at 98 Cutter Mill Rd, Great Neck Plaza, NY 11021, United States so that the drawings, takeoffs and project layouts are adjusted properly, in design and construction. With credible CMU dimension information, construction workers and architects will be able to make fewer mistakes, enhance coordination, and attain better quality masonry outputs.
FAQs
What are standard CMU dimensions in inches?
Normal CMUs are generally given in nominal size (e.g. 8 x 8 x 16), the size to which the mortar joint is added. The real size is generally 3/8 less in every direction in order to accommodate the joint.
What is the meaning of STC on CMU walls?
STC (Sound Transmission Class) is the rating of the effectiveness of a wall in stopping sound. When completely grouted and insulated, CMU walls can have a STC rating of more than 60 dB, enhancing acoustic comfort within buildings around noises.
What is the significance of ASTM C90 to CMUs?
ASTM C90 is the standard that establishes tolerable strength, density and manufacturing tolerances of load bearing CMUs. By achieving this standard, stability in performance can be predicted in structural applications.
Can CMUs improve energy performance?
Yes. Because of their thermal mass, CMU walls can help moderate indoor temperature swings, which may reduce heating and cooling demands.
When should half blocks be used?
Half blocks are used at wall ends, corners, and intersections to maintain consistent courses and reduce on-site cutting.
